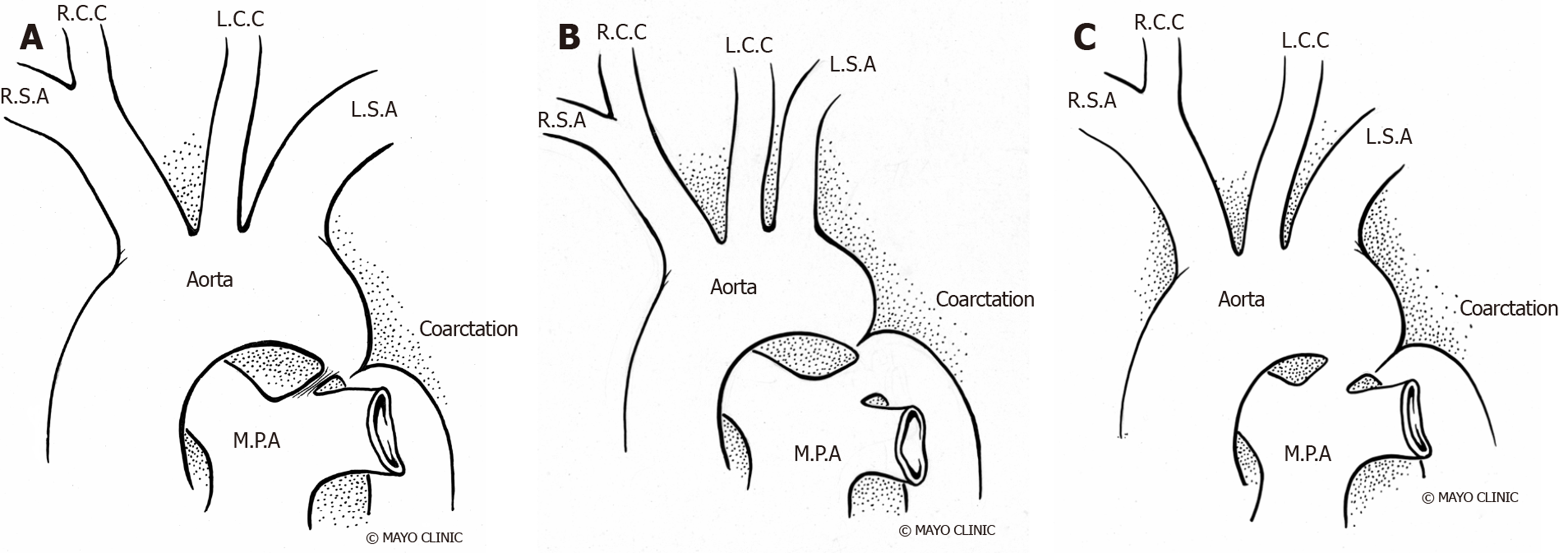
Coarctation Of Aorta Turner Syndrome
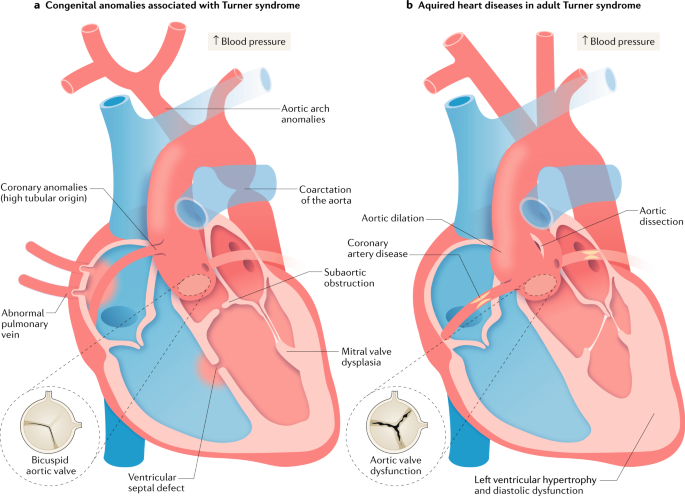
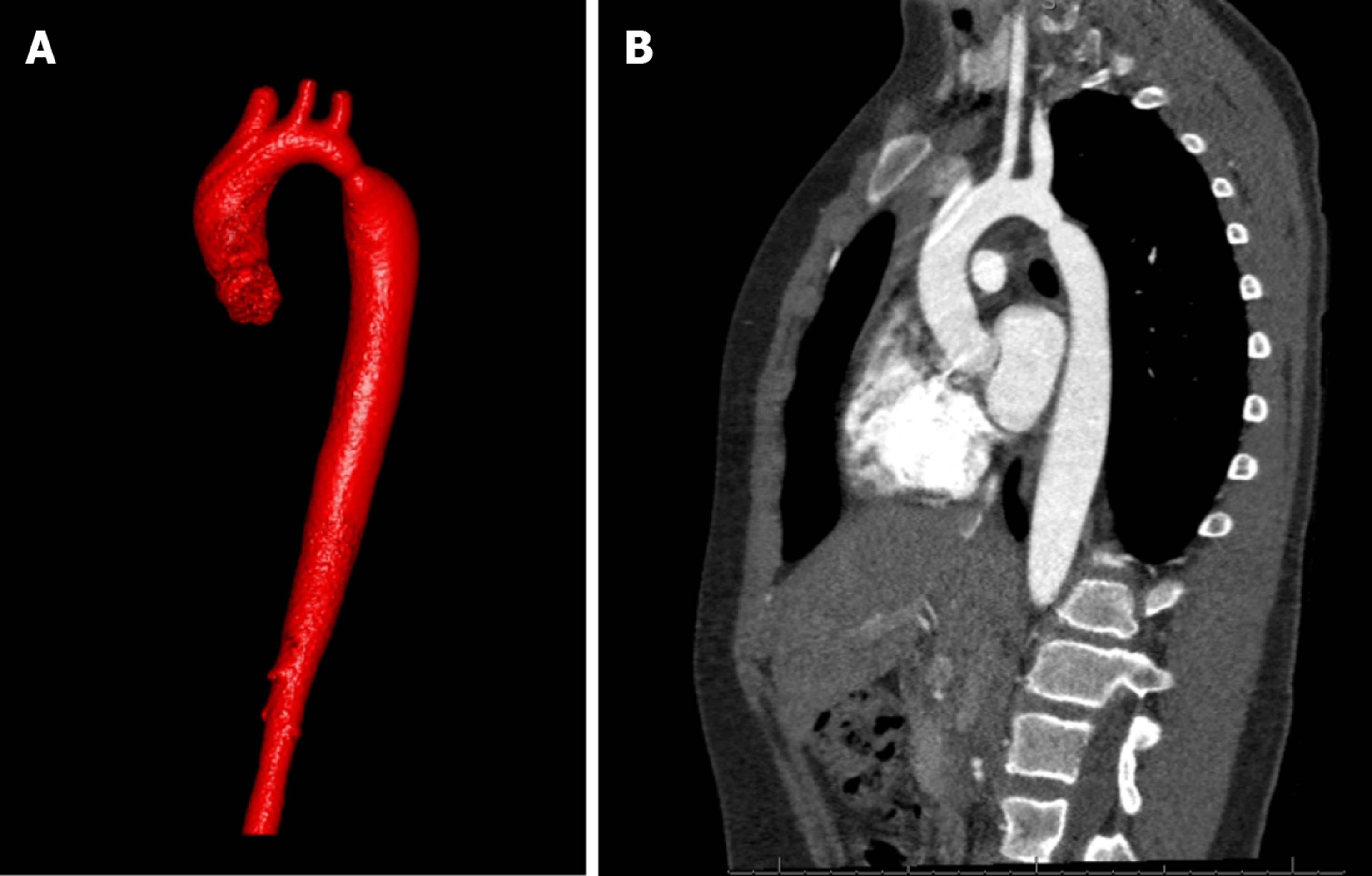
Coarctation of aorta turner syndrome. About 30 of Turner syndrome patients are diagnosed in childhood while 19 to 22 are identified as adolescents. Most commonly seen cardiovascular abnormalities are bicuspid aortic valve BAV partial anomalous pulmonary venous return elongation of the transverse aortic arch aortic coarctation and ascending aortic dilatation13 Depending on the definition the prevalence of aortic dilatation ranges from 4 to 424 5 In patients with TS aortic dissection is reported to occur six times more often compared with the general population1 Reported associated factors of aortic. In a study of 132 girls diagnosed with aortic coarctation who subsequently underwent karyo-typing Turner syndrome was diagnosed in 5320 CoA is found in 18 of patients with Turnersyndrome21 Williamssyndromeacongen-ital and multisystem genetic disorder has been.
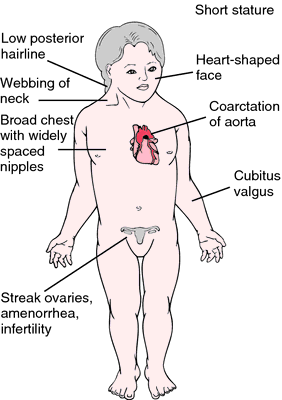
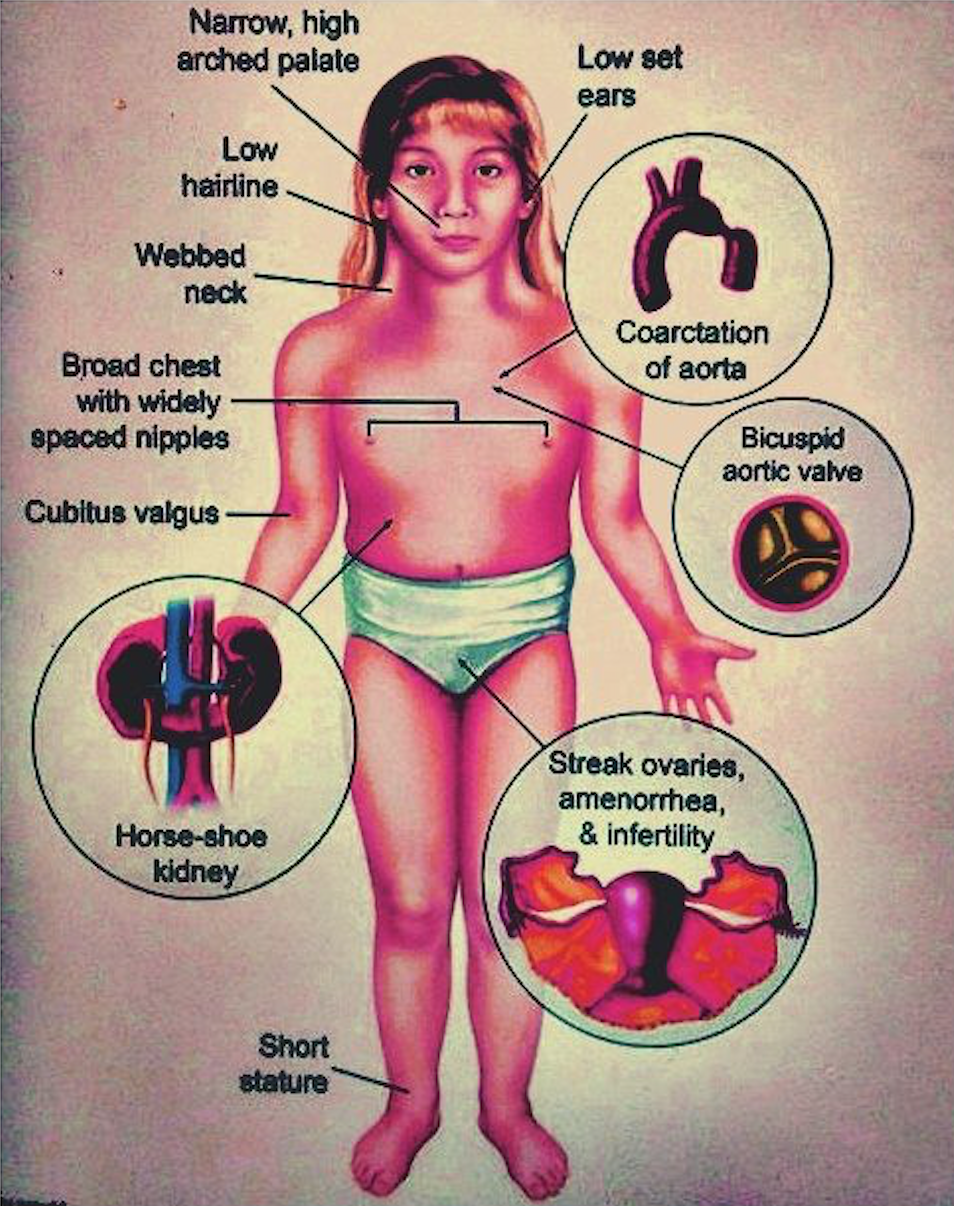
A pathologic study of fetuses with nuchal cystic hygromas hydrops fetalis and female genitalia. Beside the basic chromosomal anomaly additional risk factors like coarctation of the aorta aortic valve defects or arterial hypertension are frequently present in the affected girls. Cardiovascular abnormalities are one of the most common complications in girls and women with Turner Syndrome TS Congenital heart disease occurs in up to 50 of individuals with TS and is more common in those with a 45X karyotype.
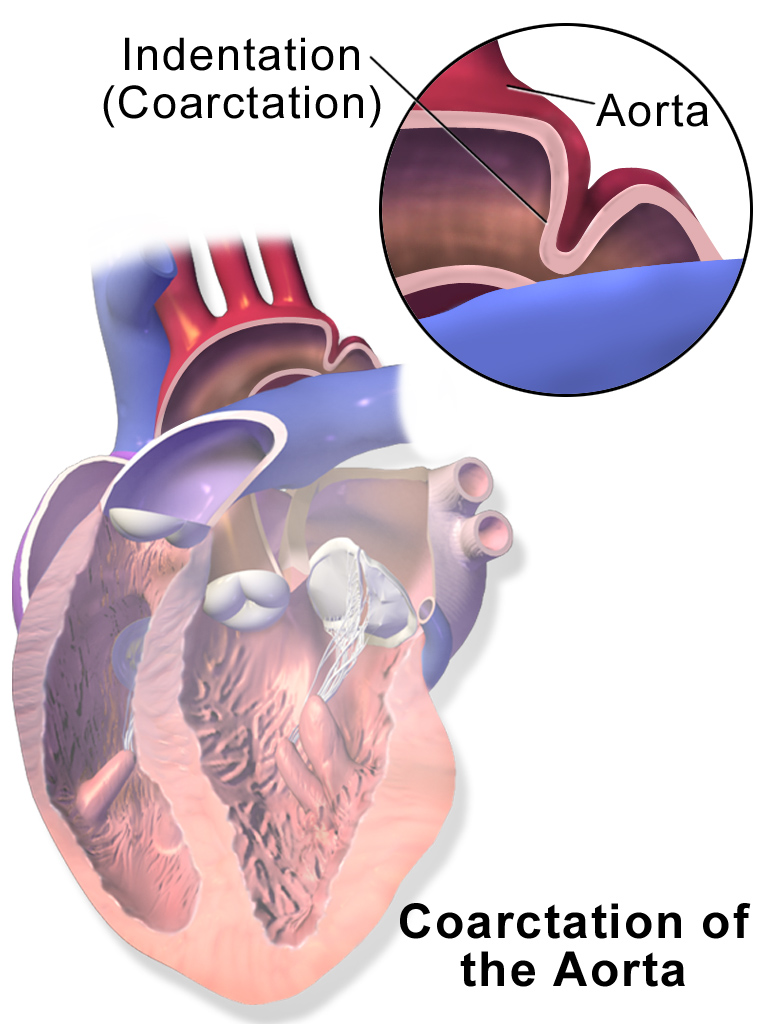
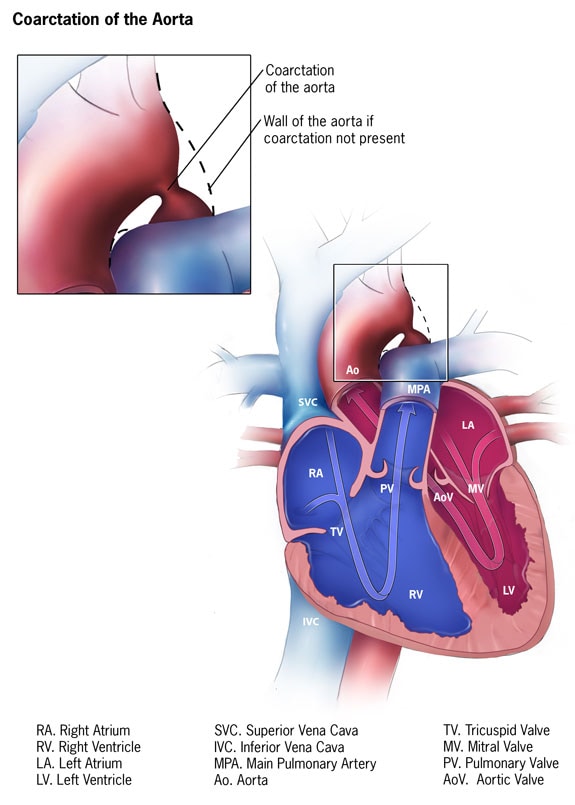
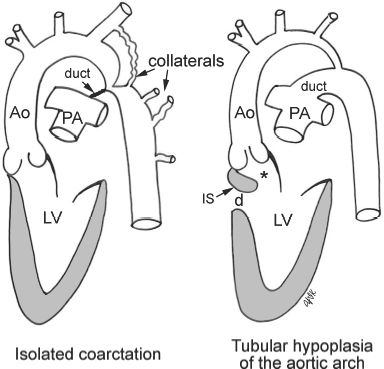
Although the most frequent cardiac lesion is coarctation of the aorta a spectrum of cardiac defects occurs which is limited almost exclusively to defects associated with decreased blood flow through the left heart. Bicuspid aortic valve is common and many have left-sided heart obstructive disease of varying severity from hypoplastic left-sided heart syndrome to minimal aortic stenosis or coarctation of the aorta. Livebirths with isolated coarctation of the aorta or transverse arch hypoplasia were included and patients with complex congenital heart.
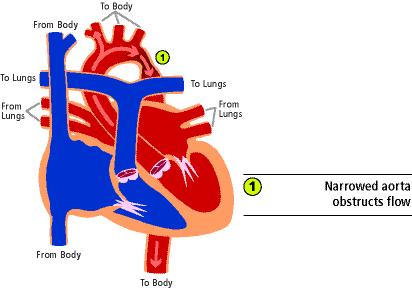
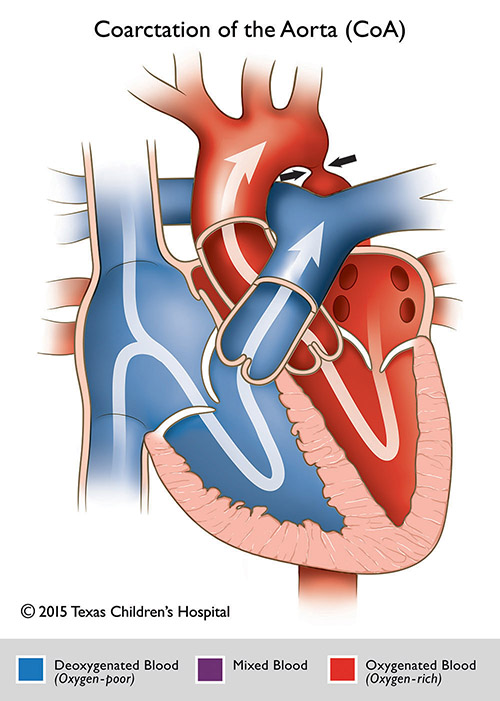
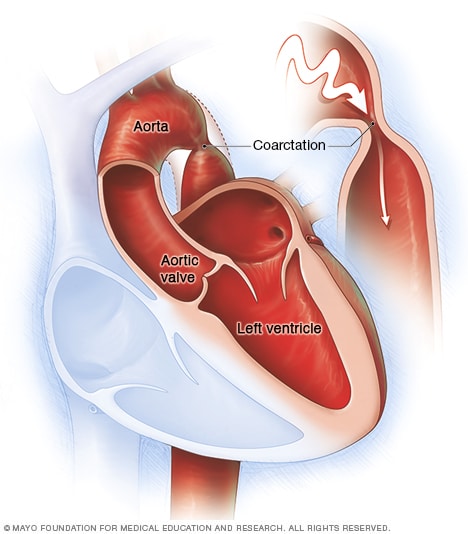
9 13 14 18 However there is a scarcity of data documenting the converse relationship. Twelve percent of Turner syndrome patients have CoA which is a risk factor for aortic dissection. Coarctation of the aorta Turner syndrome results from loss of or abnormality in the second X chromosome in a phenotypic female subject.
The rupture of dissecting aortic aneurysms is one major reason for the shorter life expectancy of patients with UTS compared to the normal population. Coarctation of the aorta in Turner syndrome. Girls and women with Turner syndrome face a lifelong struggle with both congenital heart disease and acquired cardiovascular conditions.
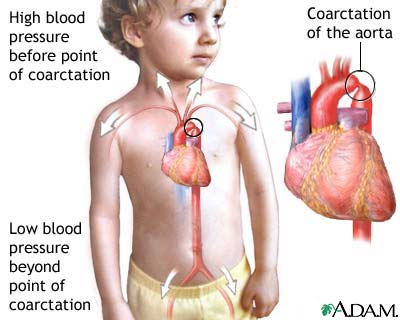
The defect appears in boys twice as often as in girls. Ravelo recently reported the results of surgical repair of coarctation of the aorta in eight patients with Turners syndrome. Coarctation of the aorta is known to be more common in girls with Turner syndrome 4-17 compared with the general population.
The Utah Birth Defects Network was used to ascertain a cohort of girls between 1997 and 2011 with coarctation of the aorta. Although the most frequent cardiac lesion is coarctation of the aorta a spectrum of cardiac defects occurs which is limited almost exclusively to defects associated with decreased blood flow through the left heart.
Coarctation of the aorta in Turner syndrome.
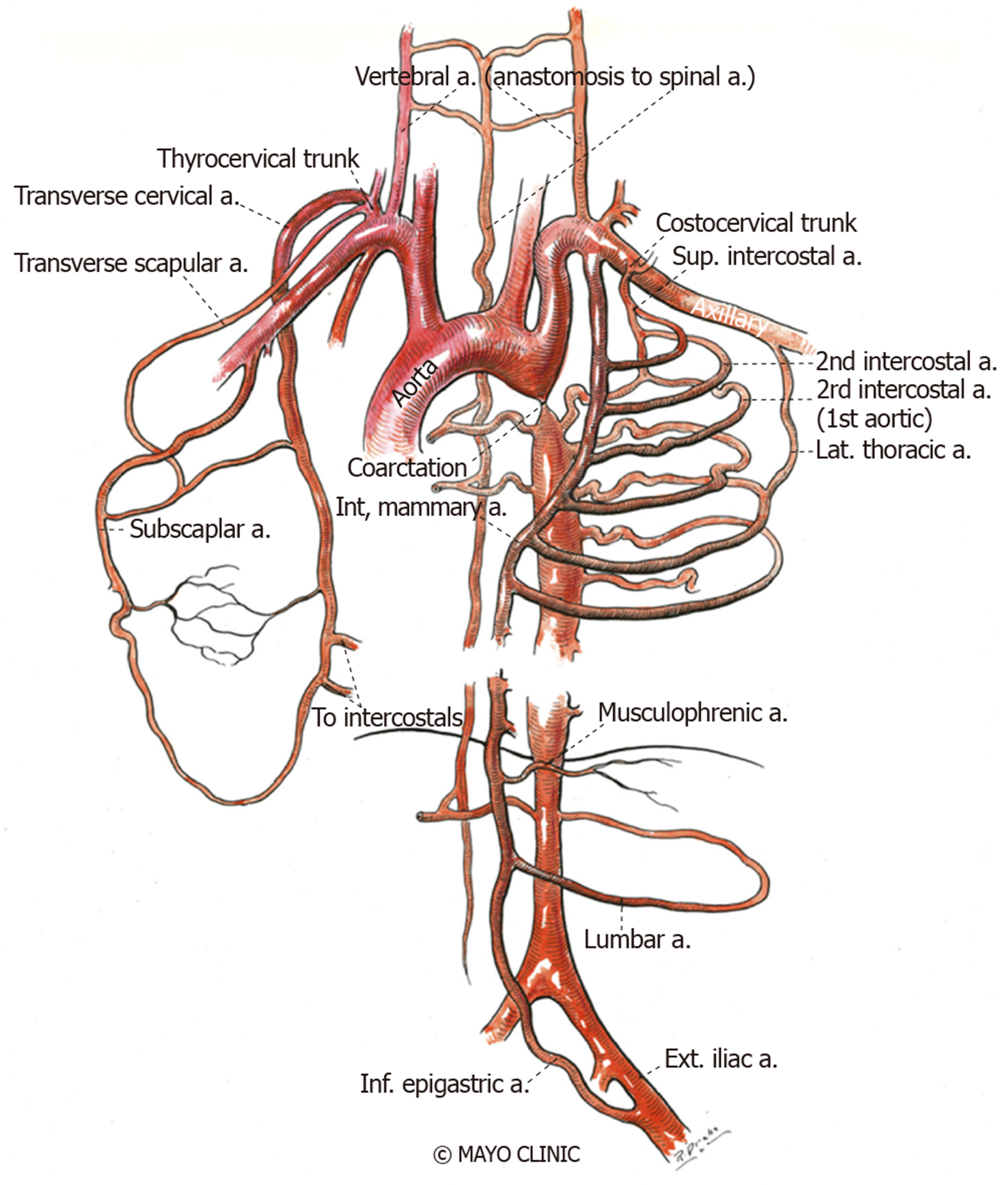
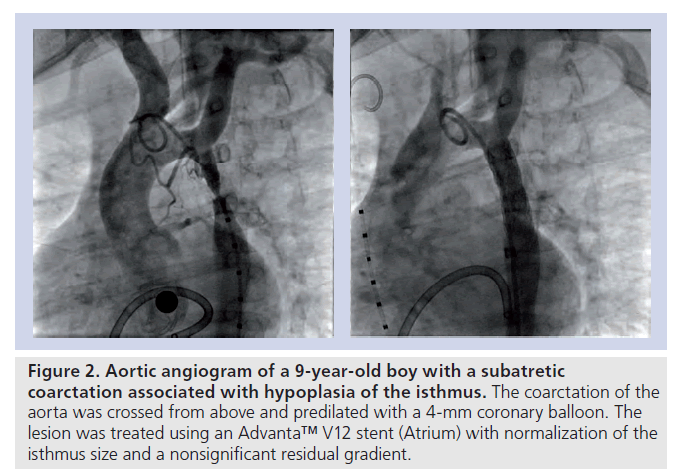
Turner syndrome has a strong association with CoA. Left-sided heart defects are most common with frequencies of. At Texas Childrens Hospital we have operated on four patients with Turners syndrome and coarctation of the aorta without complications. Livebirths with isolated coarctation of the aorta or transverse arch hypoplasia were included and patients with complex congenital heart. The rupture of dissecting aortic aneurysms is one major reason for the shorter life expectancy of patients with UTS compared to the normal population. Most of the time aortic coarctation happens with no clear reason for its cause. Although the most frequent cardiac lesion is coarctation of the aorta a spectrum of cardiac defects occurs which is limited almost exclusively to defects associated with decreased blood flow through the left heart. Coarctation of the aorta makes up about 8-11 of all congenital heart defects. Twelve percent of Turner syndrome patients have CoA which is a risk factor for aortic dissection.
Most commonly seen cardiovascular abnormalities are bicuspid aortic valve BAV partial anomalous pulmonary venous return elongation of the transverse aortic arch aortic coarctation and ascending aortic dilatation13 Depending on the definition the prevalence of aortic dilatation ranges from 4 to 424 5 In patients with TS aortic dissection is reported to occur six times more often compared with the general population1 Reported associated factors of aortic. Bicuspid aortic valve is common and many have left-sided heart obstructive disease of varying severity from hypoplastic left-sided heart syndrome to minimal aortic stenosis or coarctation of the aorta. Turner syndrome has a strong association with CoA. Livebirths with isolated coarctation of the aorta or transverse arch hypoplasia were included and patients with complex congenital heart. Although the most frequent cardiac lesion is coarctation of the aorta a spectrum of cardiac defects occurs which is limited almost exclusively to defects associated with decreased blood flow through the left heart. Girls and women with Turner syndrome face a lifelong struggle with both congenital heart disease and acquired cardiovascular conditions. Left-sided heart defects are most common with frequencies of.


























Post a Comment for "Coarctation Of Aorta Turner Syndrome"