Liver Disease Macrocytic Anemia
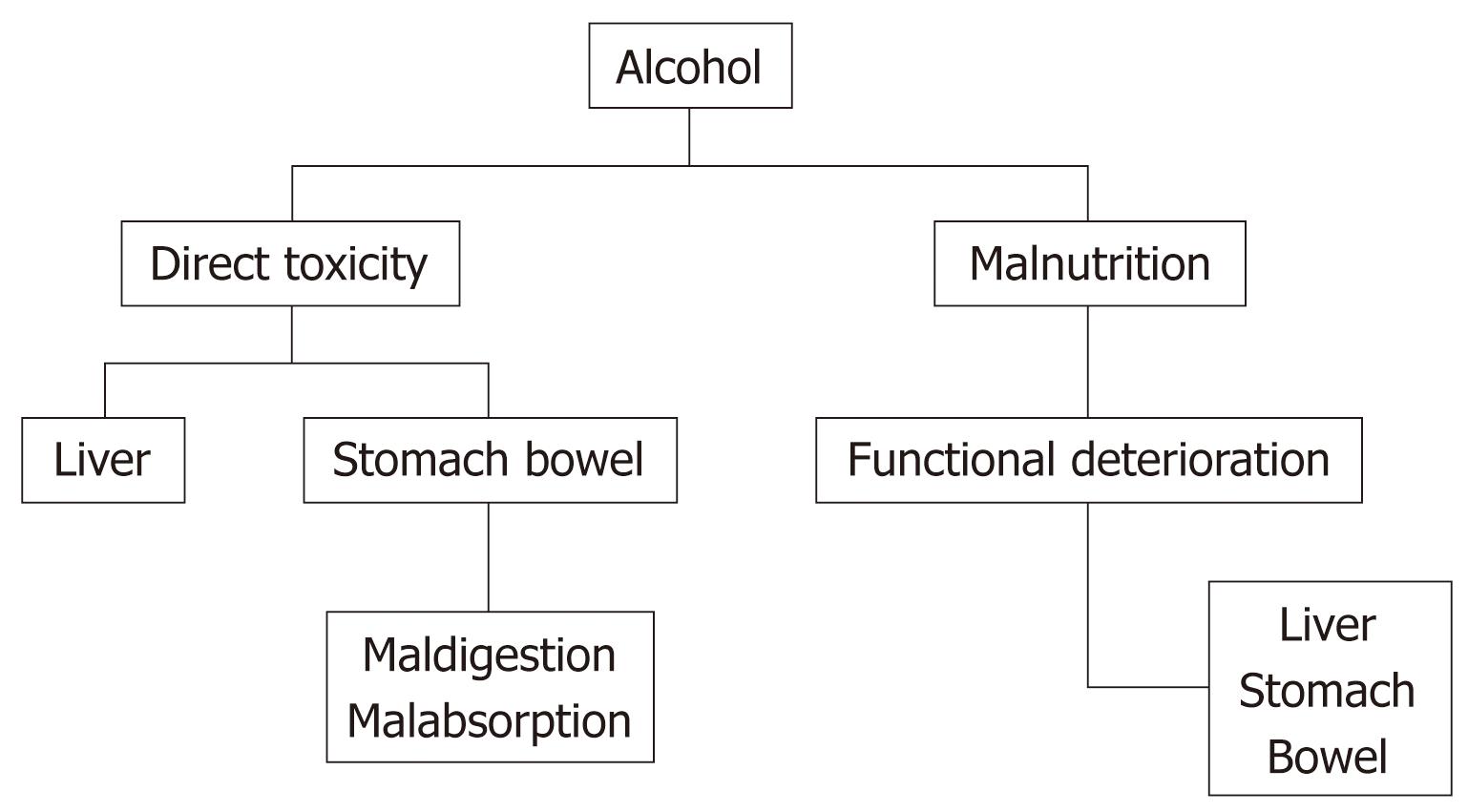
Liver disease macrocytic anemia. Macrocytosis may be physiologically normal as in the newborn Chapter 43 or the result of a pathologic condition as in liver disease chronic alcoholism or bone marrow failure. The skin was moderately jaundiced icteric index 45. The etiology of anemia in liver disease is diverse and often multifactorial.
Alcohol a common etiologic factor of chronic liver disease. A man aged 50 showed a clinical picture of advanced hepatic cirrhosis together with signs strongly suggestive of pernicious anemia. The similarities and dissimilarities to Addisonian pernicious anemia are reviewed.
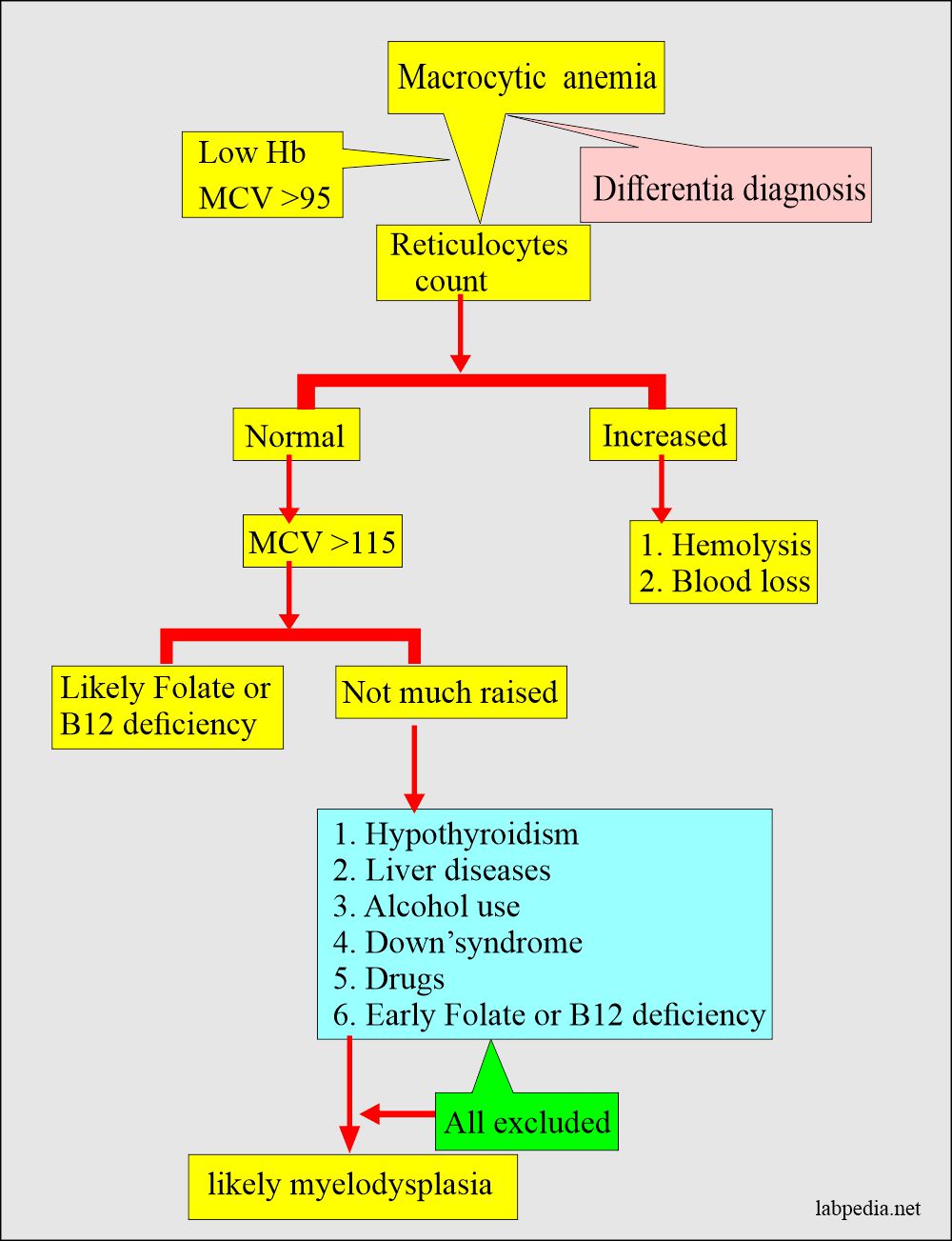
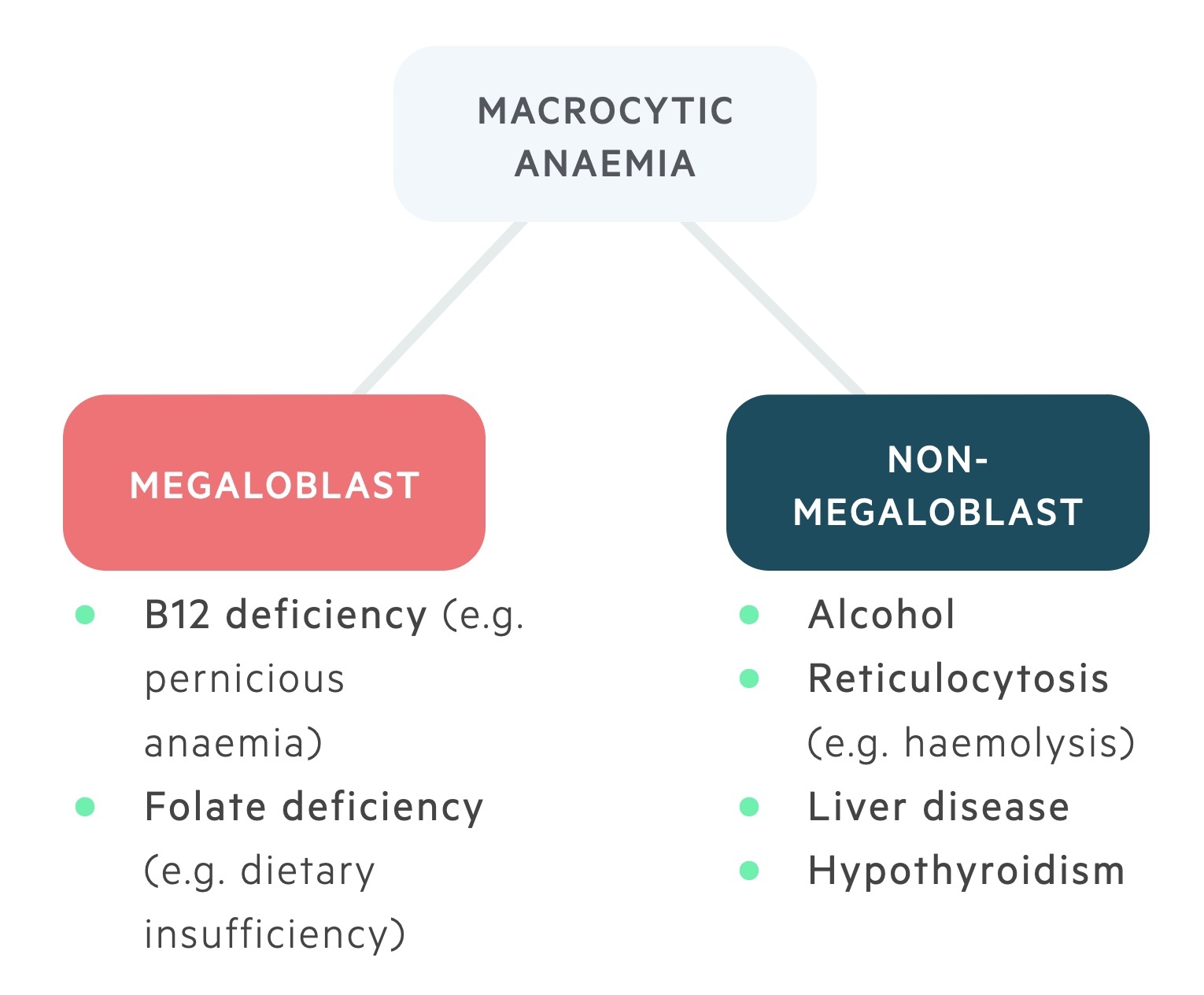
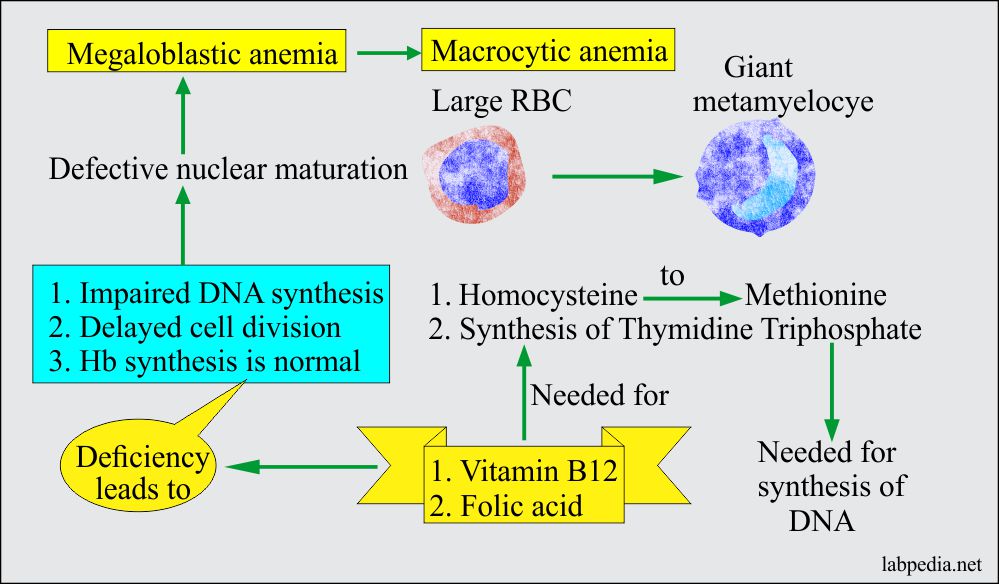
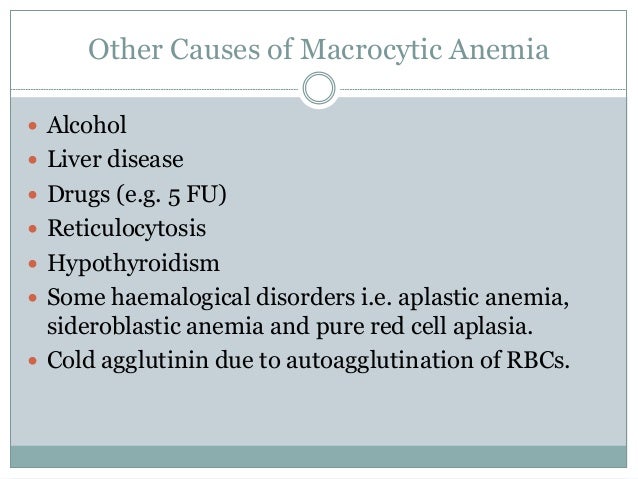
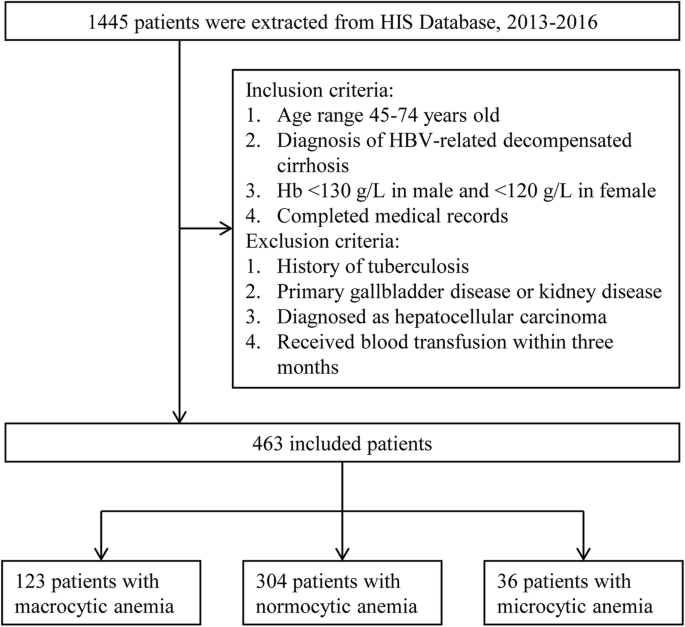
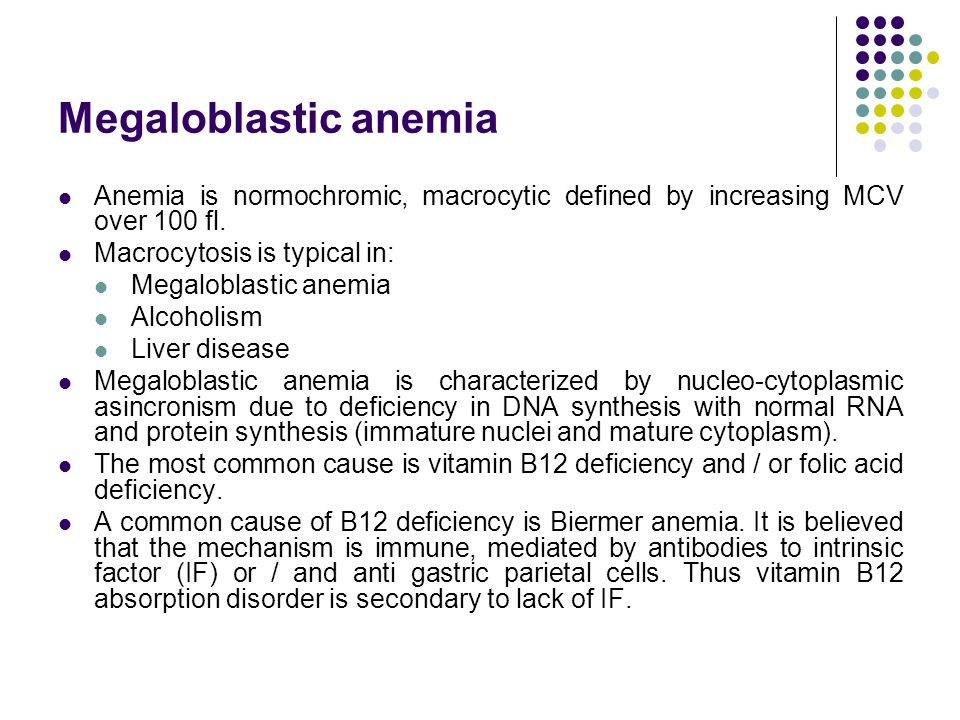
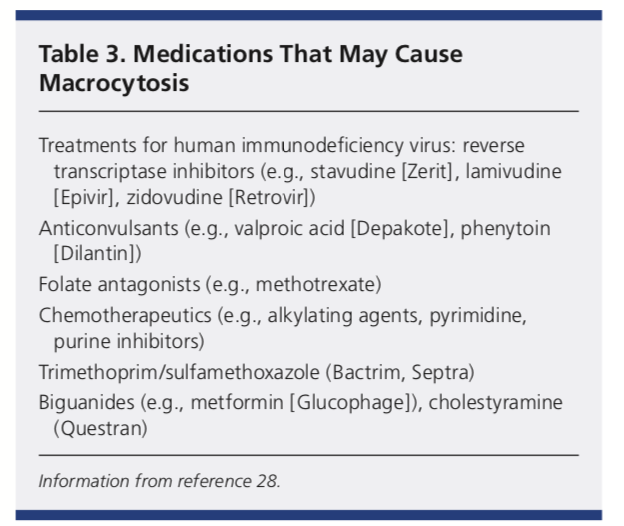
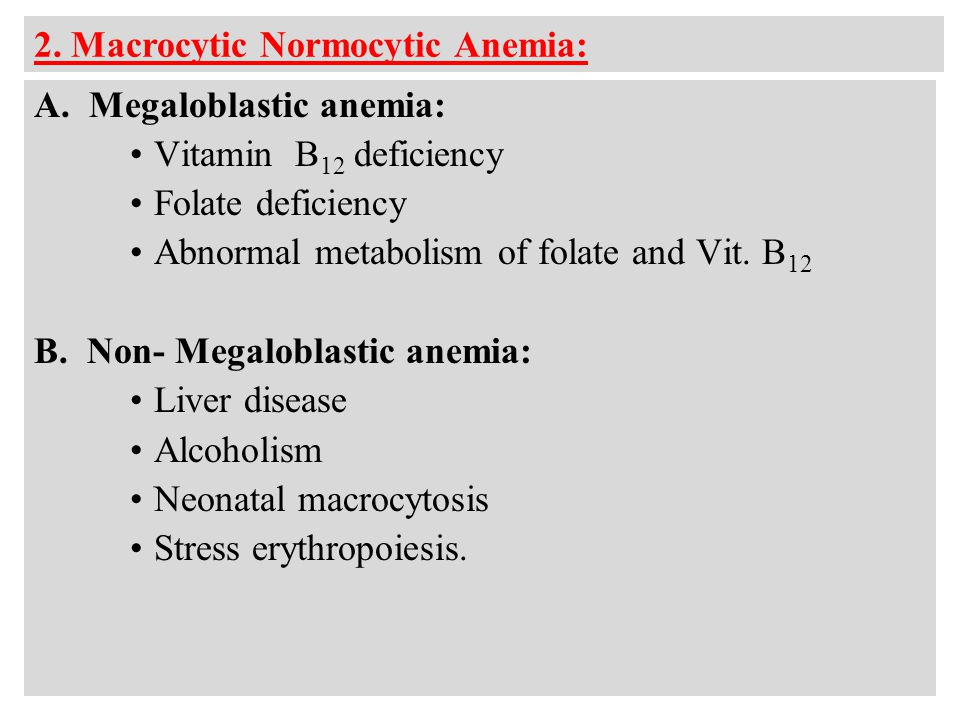
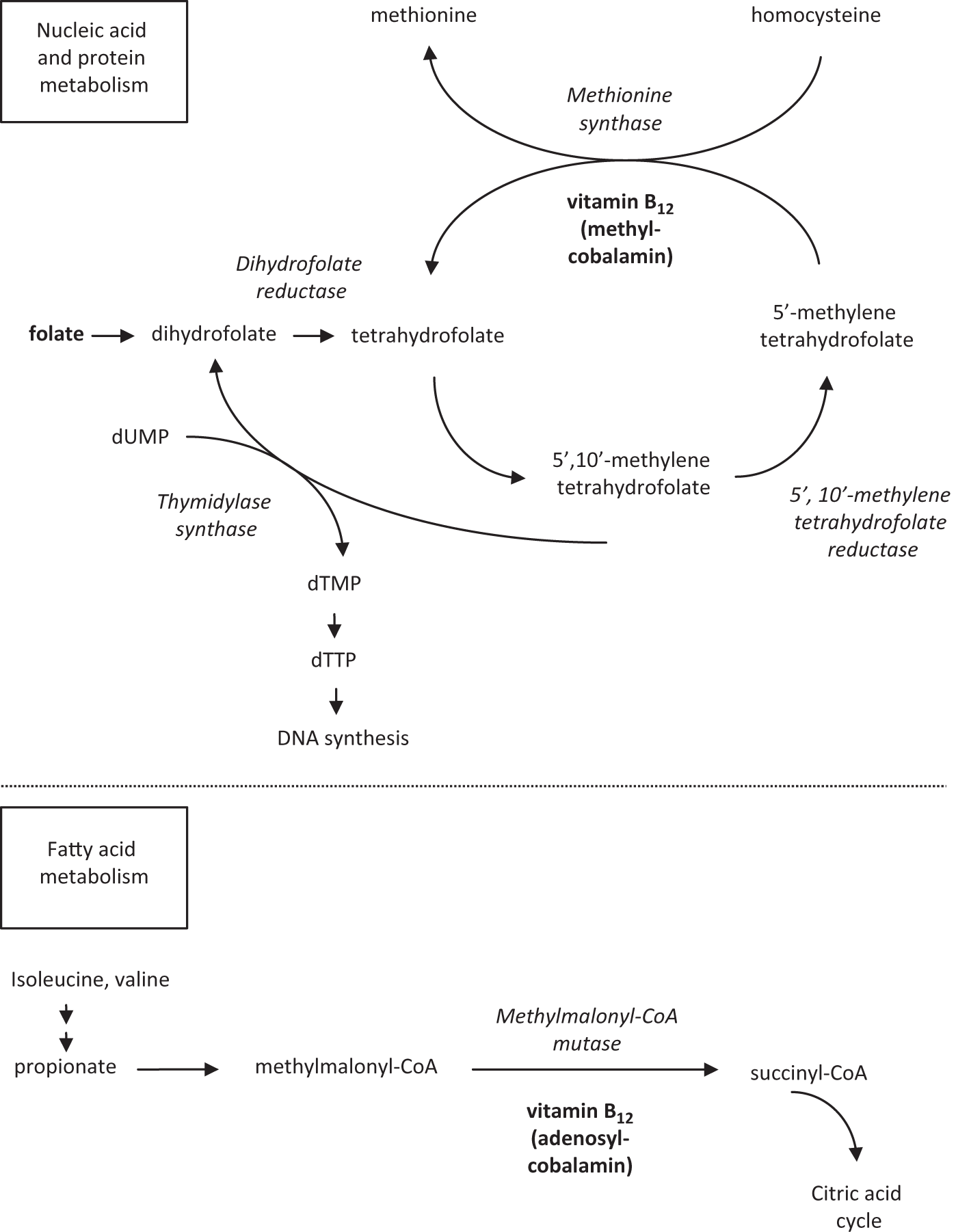
The aim of the present study was to determine the association between macrocytic anemia and the severity of liver impairment in patients with HBV-related decompensated cirrhosis according to the Model for End Stage Liver Disease MELD score. In megaloblastic anemia the MCV exceeds 95 fL. Alcoholism and liver disease are both causes of nonmegaloblastic macrocytic anemia as well as drugs like 5-fluorouracil.
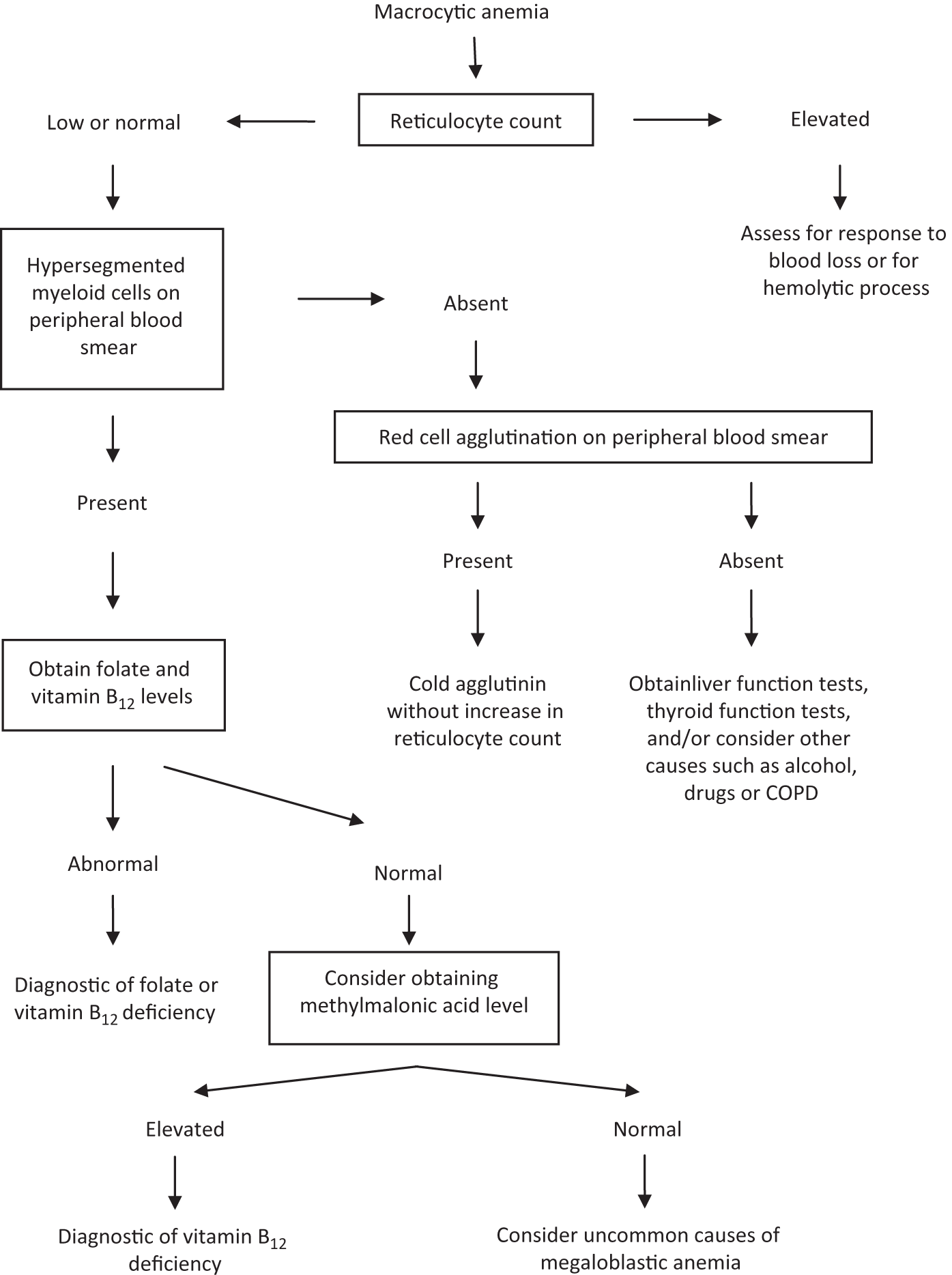
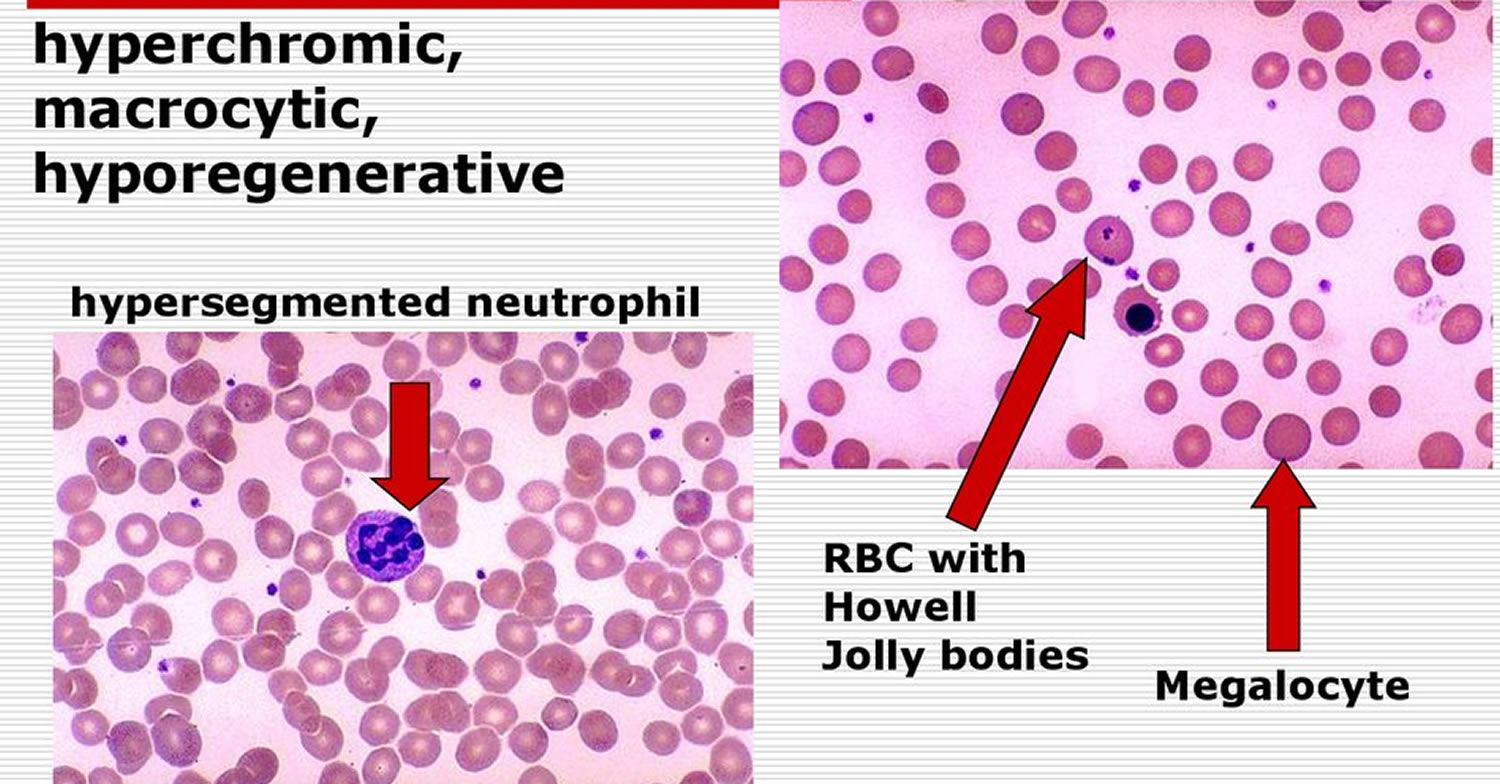
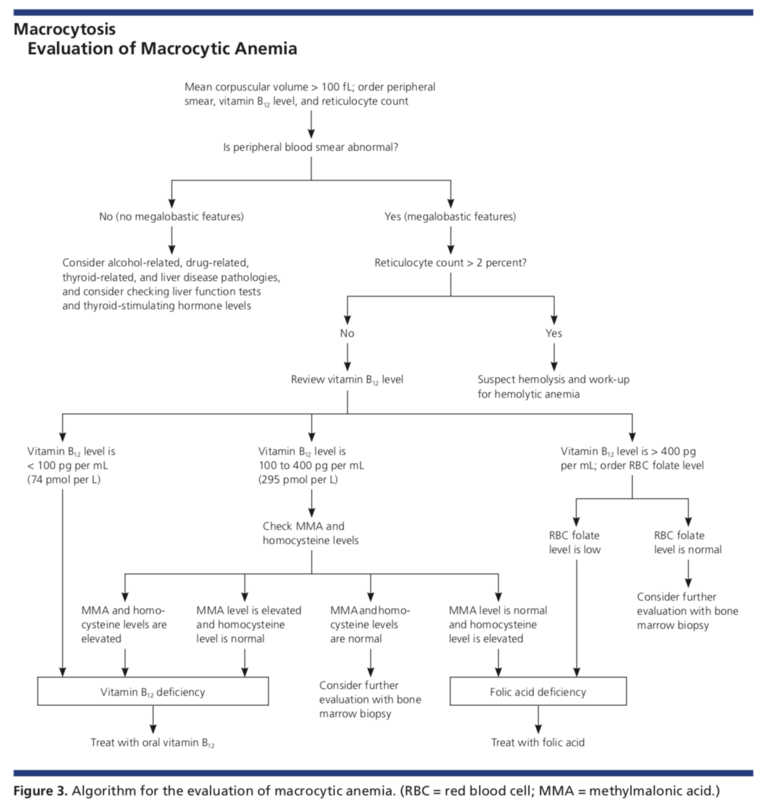
Macrocytosis with an MCV of about 100 to 105 fLcell can occur with chronic alcohol use in the absence of folate deficiency. There are no hypersegmented neutrophils or megaloblastic changes in the. Figure 1812 presents an algorithm for.
The liver was markedly enlarged and nodular. Your doctor will run tests to. Both treatments have proved unsuccessful.
Round macrocytes are commonly seen in a variety of chronic illnesses and round target-appearing macrocytes are characteristic of liver disease such as hepatitis obstructive jaundice and acute and chronic alcoholism with liver disease figure 1. Alcohol a common etiologic factor of chronic liver disease is toxic to. Even though the pathogenesis of this disorder is unclear attempts have been made to correct macrocytosis with vitamin B 12 or folic acid.
There were in addition glossitis combined sclerosis and a macrocytic type of anemia. Like other types of anemia macrocytic anemia means that the red blood cells.
While nutrient deficiencies cause most macrocytic anemias other underlying conditions may cause the deficiencies.
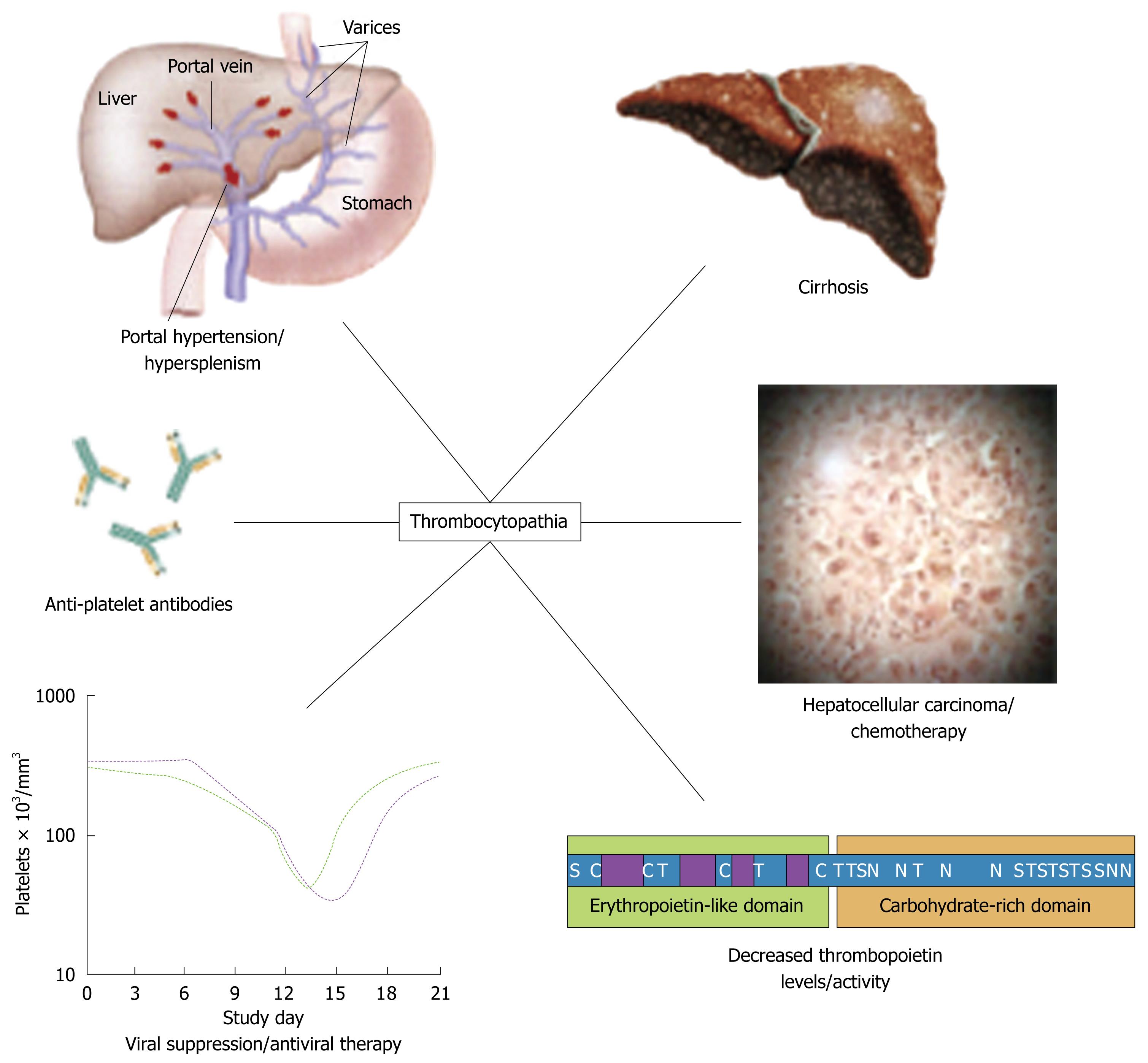
E macrocytes tend to be oval. There are no hypersegmented neutrophils or megaloblastic changes in the. We studied the red cell and vitamin status in 423 consecutive patients with various liver diseases including 31 with acute viral hepatitis. Splenomegaly which is usually caused by portal hypertension in patients with chronic liver disease may lead to secondary hemolysis an increase in plasma volume macrocytosis and megaloblastic anemia. Attention is drawn to the importance of considering chronic liver disease cirrhosis in particular in the differential. Alcohol a common etiologic factor of chronic liver disease. The incidence course prognostic significance pathologic findings treatment and pathogenesis of the macrocytic anemia occurring in advanced or wide-spread liver disease are discussed. Macrocytosis due to excess RBC membrane occurs in patients with chronic liver disease when cholesterol esterification is defective. Like other types of anemia macrocytic anemia means that the red blood cells.
Both treatments have proved unsuccessful. E RBCs vary considerably in size and shape. Macrocytosis is most commonly associated with vitamin B12 and folic acid deficiency followed by alcoholism liver disease and other pathologic conditions. There were in addition glossitis combined sclerosis and a macrocytic type of anemia. The similarities and dissimilarities to Addisonian pernicious anemia are reviewed. Macrocytosis due to excess RBC membrane occurs in patients with chronic liver disease when cholesterol esterification is defective. In liver disease macrocytosis is also mild and uniform.































Post a Comment for "Liver Disease Macrocytic Anemia"